Introduction
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder among women of reproductive age, affecting approximately 10% of women worldwide. This condition not only impacts a woman’s health but also poses significant challenges to her fertility. In this article, we will explore the nuances of PCOS, its implications on fertility, and the various strategies for management and treatment.
What is PCOS?
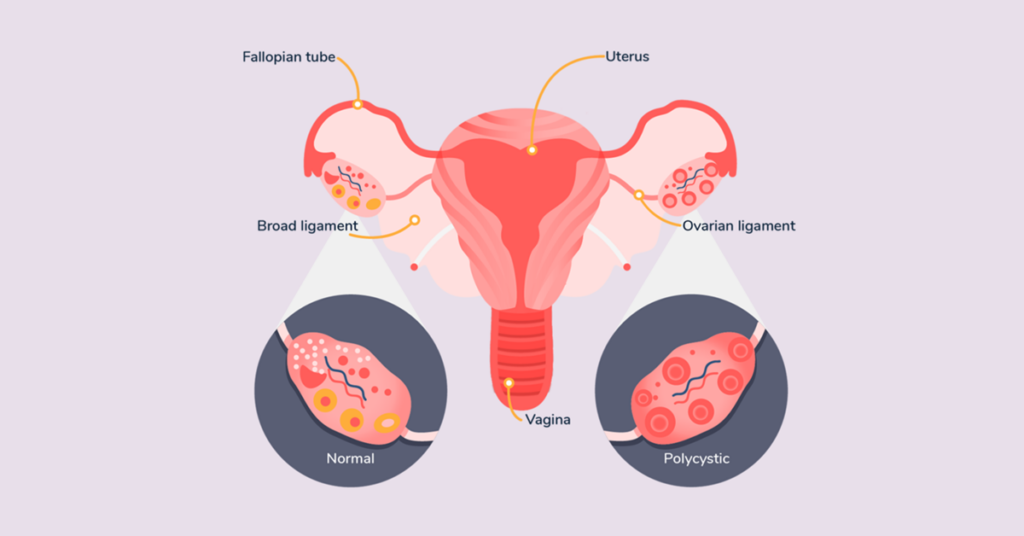
PCOS is characterized by a combination of symptoms resulting from hormonal imbalances, including elevated levels of male hormones (androgens). Common symptoms include irregular menstrual cycles, excessive hair growth, acne, and obesity. Women with PCOS often have multiple small cysts on their ovaries, as seen in ultrasounds, although cysts are not required for diagnosis. Diagnosis typically involves a review of medical history, physical examination, blood tests, and an ultrasound.
PCOS and Fertility Challenges
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) significantly impacts fertility, mainly due to its effects on ovulation and hormonal balance. Here are the key points highlighting these challenges:
1. Irregular Ovulation
Women with PCOS often experience irregular or absent ovulation (anovulation), which is a leading cause of infertility. This irregularity makes it challenging to predict fertile windows for conception.
2. Hormonal Imbalances
PCOS is characterized by an excess of androgens (male hormones) which can disrupt the normal ovulatory cycle and hinder the ability to conceive.
3. Insulin Resistance
A common feature in PCOS, insulin resistance can exacerbate hormonal imbalances, further affecting ovulation and fertility.
4. Obesity and Weight Issues
Many women with PCOS struggle with obesity, which can independently affect fertility by altering hormone levels and menstrual cycles.
5. Increased Risk of Miscarriage
Research indicates a higher rate of miscarriage in women with PCOS, likely due to hormonal imbalances and other metabolic issues related to the syndrome.
6. Chronic Inflammation
PCOS is often associated with low-grade inflammation, which can impact ovary function and ultimately fertility.
7. Endometrial Issues
Due to irregular periods, the endometrium (lining of the uterus) can be affected, potentially leading to complications with implantation or increased risk of endometrial cancer, which indirectly affects long-term fertility.
Addressing these challenges often requires a multifaceted approach, including lifestyle changes, medical intervention, and consistent monitoring under the guidance of healthcare professionals.
Also Read- A Guide to Surrogacy
Lifestyle and Diet Management for PCOS

Managing PCOS effectively involves targeted lifestyle and dietary changes:
1. Weight Management
Aim for moderate weight loss if overweight, as it can significantly improve hormonal balance and ovulation.
2. Balanced Diet
Focus on a diet rich in whole foods, high in fiber, and low in processed sugars and unhealthy fats.
3. Regular Exercise
Incorporate both cardio and strength training exercises to improve insulin sensitivity and weight management.
4. Low-Glycemic Foods
Choose foods that have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels to manage insulin resistance.
5. Consistent Meals
Eating at regular intervals helps regulate blood sugar and insulin levels.
6. Inclusion of Omega-3 Fats
Include omega-3 rich foods like fish, nuts, and seeds, which can help manage inflammation associated with PCOS.
Medical Treatments and Interventions
Medical treatments for PCOS aim to restore ovulation and balance hormones. Common treatments include:
1. Metformin
Originally used to treat Type 2 Diabetes, Metformin can improve insulin resistance and ovulation in women with PCOS.
2. Clomiphene Citrate
A fertility drug that induces ovulation.
3. Letrozole
A newer treatment that may be more effective than Clomiphene in inducing ovulation.
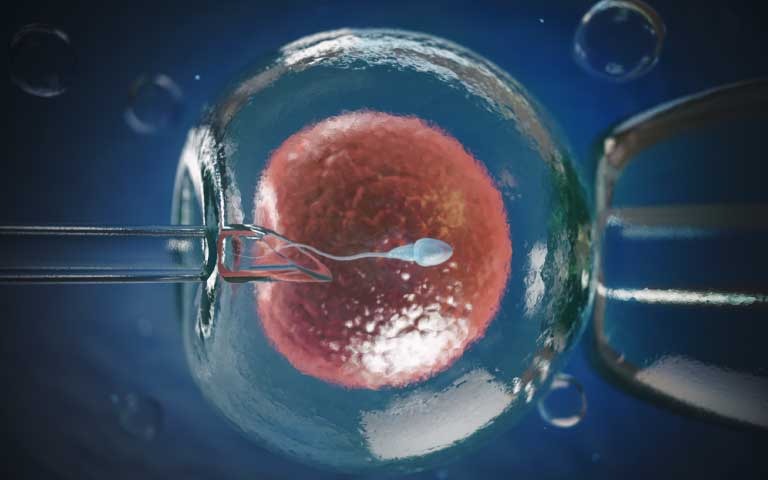
4. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
Recommended when other treatments fail, IVF can be an effective way to achieve pregnancy for women with PCOS. Recent advancements in PCOS treatment also include the use of inositols, which are supplements that can help improve insulin resistance and ovulation.
Coping Mechanisms and Support
Coping with the challenges of PCOS, especially when dealing with fertility issues, requires a holistic approach that includes both physical and emotional support:
1. Seek Professional Guidance
Regular consultations with healthcare providers, including gynecologists, endocrinologists, and dietitians, are crucial for managing PCOS symptoms and fertility concerns.
2. Join Support Groups
Connecting with others who are experiencing similar challenges can provide emotional support, practical advice, and a sense of community.
3. Mental Health Care
Consider therapy or counseling to help cope with the stress, anxiety, or depression that can accompany PCOS and fertility struggles.
4. Stress Management Techniques
Incorporate stress-reduction practices such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises into your routine.
5. Educate Yourself
Understanding PCOS and its implications on fertility can empower you to make informed decisions about your health and treatment options.
6. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep can help manage PCOS symptoms and improve overall well-being.
7. Mind-Body Therapies
Alternative therapies like acupuncture or massage may provide relief from symptoms and improve mental well-being.
8. Open Communication
Discuss your feelings and experiences with friends, family, or your partner to foster understanding and support.
By combining medical treatment with these supportive strategies, individuals with PCOS can better manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Conclusion
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) presents unique challenges, particularly regarding fertility, but it’s important to remember that it is a manageable condition. By adopting a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and emotional support, women with PCOS can effectively navigate these challenges. Embracing a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management can significantly improve symptoms and fertility outcomes.
Additionally, seeking guidance from healthcare professionals and support from peers can provide invaluable resources and comfort. Understanding, patience, and perseverance are key in this journey. With the right strategies and support, many women with PCOS go on to lead healthy lives and successfully achieve their fertility goals.